-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Module 0, Install GeoDMS GUI and setup a configuration


learning objective: Install a GeoDMS version and work with a configuration on your local machine
- Download a version of the GeoDMS, we usually advise the most recent version.
- Install the software, see Installation Instructions up to and including part I.
- Download your first configuration here
- Unzip it in a project-specific folder, which we call the ProjDir-folder, for example "C:/ProjDir/FirstConfig".
- The root configuration file to be opened is usually located in the cfg subfolder of the ProjDir, also called the ConfigDir, and often called something like root.dms. In this example, the file is called: basics_my_first_geodms_project.dms. The file to be opened is like: "C:/ProjDir/FirstConfig/cfg/basics_my_first_geodms_project.dms". For a broader overview of the suggested folder structures, see Folders and Placeholders.
- Start the installed GeoDMS GUI
- Go to the menu option: File > Open Configuration File, navigate to and open the basics_my_first_geodms_project.dms file.
- Select the my_first_param parameter in the treeview (at the left) and double-click on this item to see the contents in a table. Move your mouse to the right border of the table and keep the mouse pressed to adjust the column width to make the text fit in the table.
Your GeoDMS GUI should now look like this:

In the GeoDMS GUI, relevant options can be set with the menu option Settings. Most default settings are fine, but some settings are regularly overruled.
In the GeoDMS we often refer to a SourceData folder (for read-only source files) and a LocalData folder (for (intermediary) results.
In configurations %LocalDataDir% and %SourceDataDir% are Placeholders.
The machine-specific drives/folders for LocalDataDir and SourceDataDir can be set with the Settings > Local machine Options:

By default, the GeoDMS looks for LocalData in D:\LocalData and SourceData in D:\SourceData. You can configure your machine-specific folders here. We advise to configure the LocalDataDir not to a network drive.
From the GeoDMS GUI treeview, you can activate the corresponding line in a configuration file for a selected item. Use the CTRL + e keyboard combination or the pop-up menu option (mouse right-clicking) > Open in Editor.
We recommend using the text editor: Notepad++,. A language file for each software release is available in the same folder as the installed GeoDMS software (%programfiles%/ObjectVision/GeoDmsVersion).
For instructions on how to import the language file into Notepad++ see Setup GeoDMS language file in Notepad++.
To ensure GeoDMS understands where Notepad++ is installed, select your application with the folder button next to the application. The application control shows the path of the editor, e.g., "C:/Program Files/Notepad++/Notepad++.exe"
Parameters can be set to open the correct file and position in the file. With the button: Set default parameters for the editor, the advised settings are set, e.g., "%F" -n%L for Notepad++. See the documentation for your editor if other parameters are desired.

To test this, select the item: my_first_param in the treeview and activate from the pop-up menu (right mouse click) the option: Open in Editor (you can also use the Crtl - E key combination). The file editor should now be opened with the cursor on the line of the selected item. If you installed the GeoDMS language files, your editor should look like this:
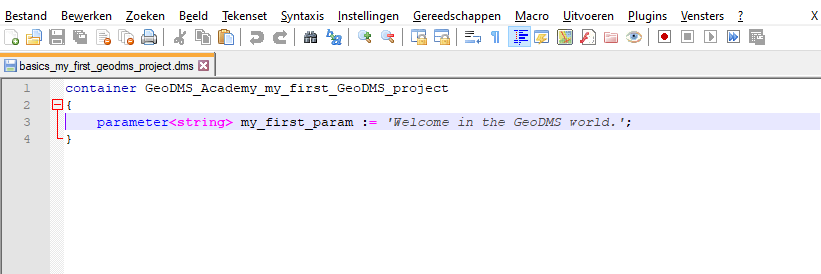
Edit the text: Welcome in the GeoDMS world, save the changes and reopen the configuration.
This is a common way of working with GeoDMS configuration files.
Go to next module: Module 1, Learning the basic concepts of GeoDMS
GeoDMS Academy

- 0: Install GeoDMS GUI and setup a configuration
- 1: Learning the basic concepts of GeoDMS
- 2: Loading and storing data sources
- 3: Basic analyses with vector data (WORK IN PROGRESS)
- 4: Basic analyses with grid data (WORK IN PROGRESS)
- 5a: Working with networks over a road network
- 5b: Working with networks in a public transport setting
- 6: Allocating land-use