-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 50
Grid Local Grid
The local grid defines the indexing for a single part of the domain decomposition.
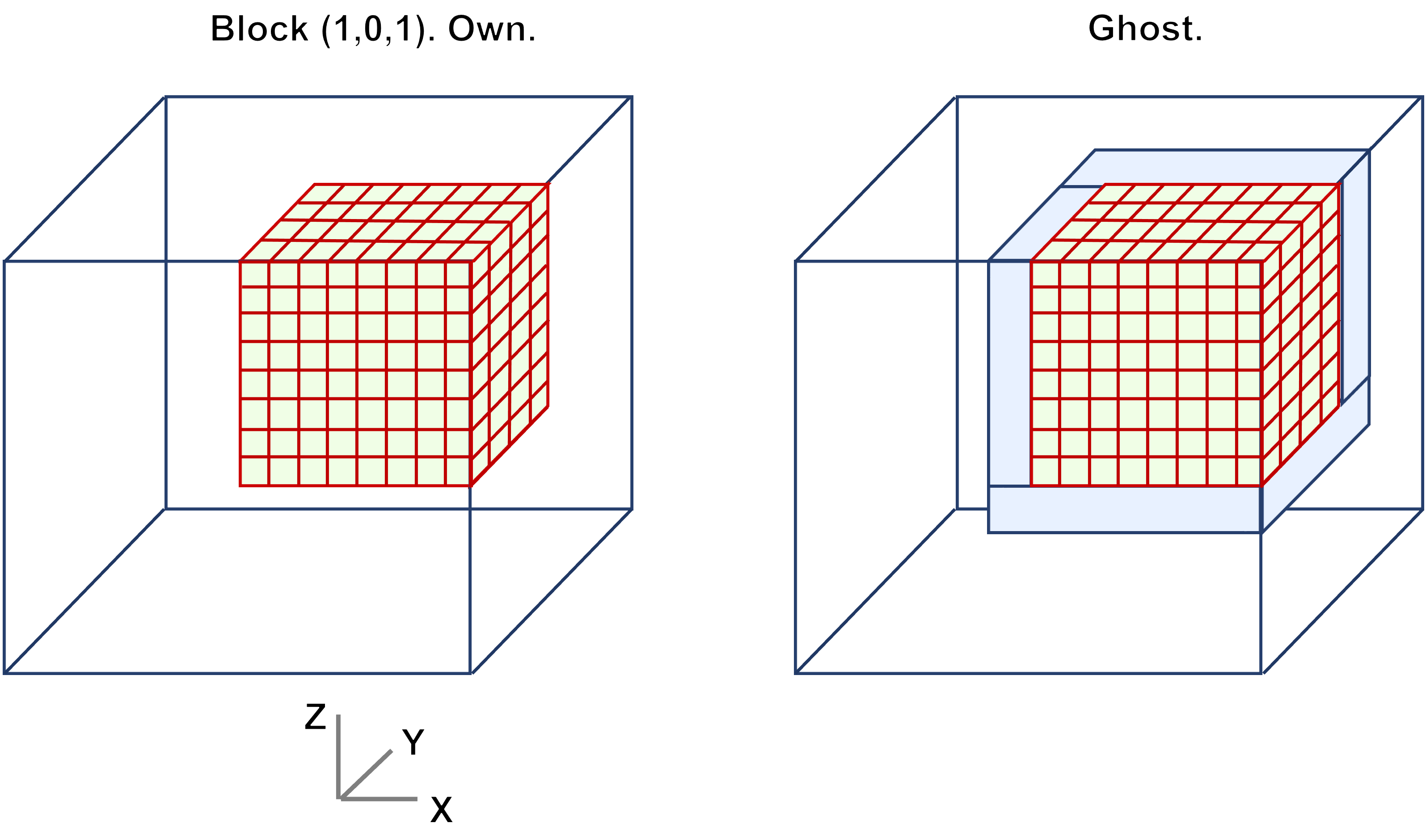
The figure below highlights one local domain of a total system, where indexing information is again shown in red. The ghosted information from neighboring ranks can be optionally used (right):
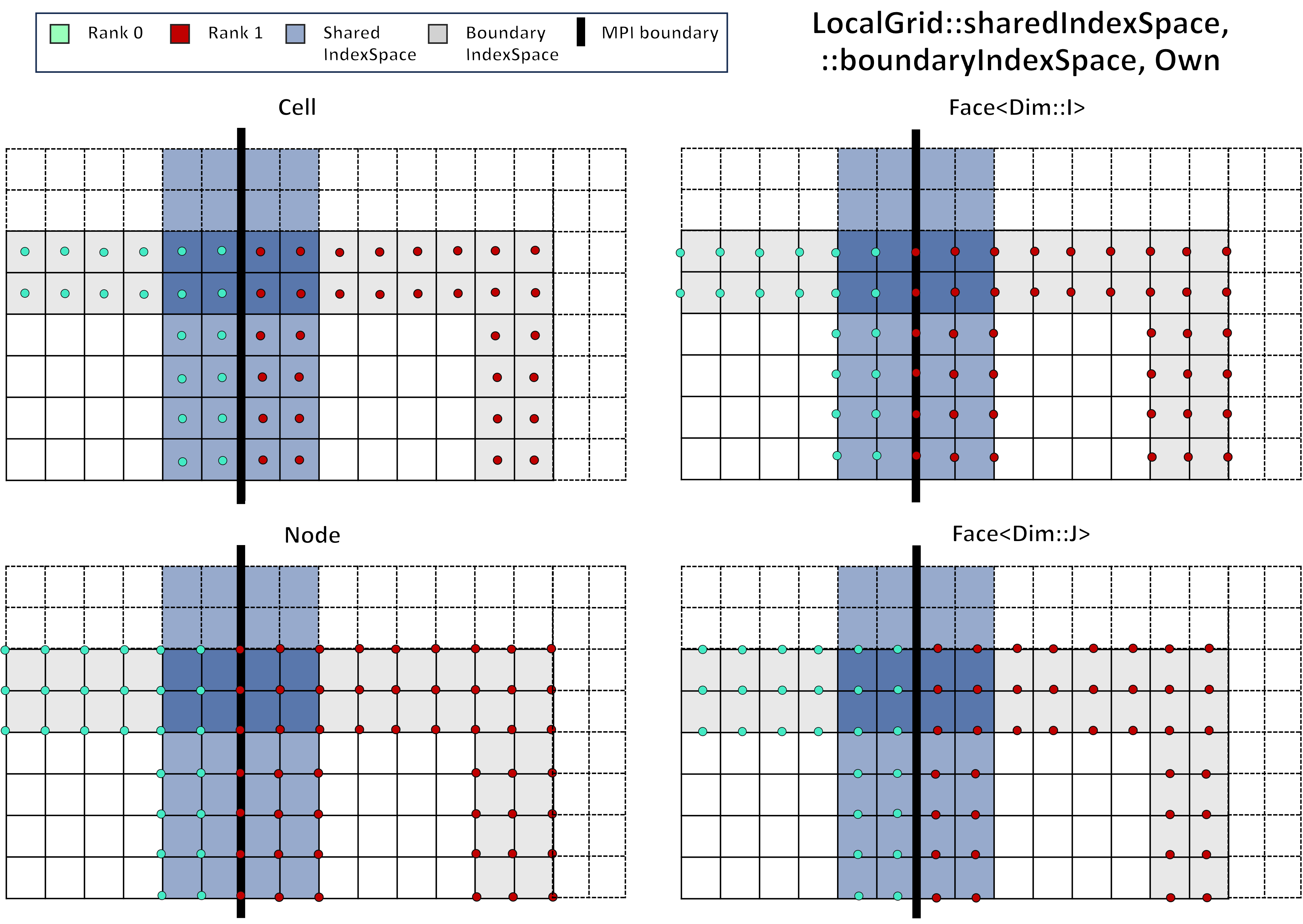
The local grid contains many index spaces in order to iterate in parallel. The primary index spaces for a given entity (Cell, Node, Face<Dim>, Edge<Dim>) can use either Local or Global indexing and either exclude ghosted entities (Own):
 or include ghosted entites (
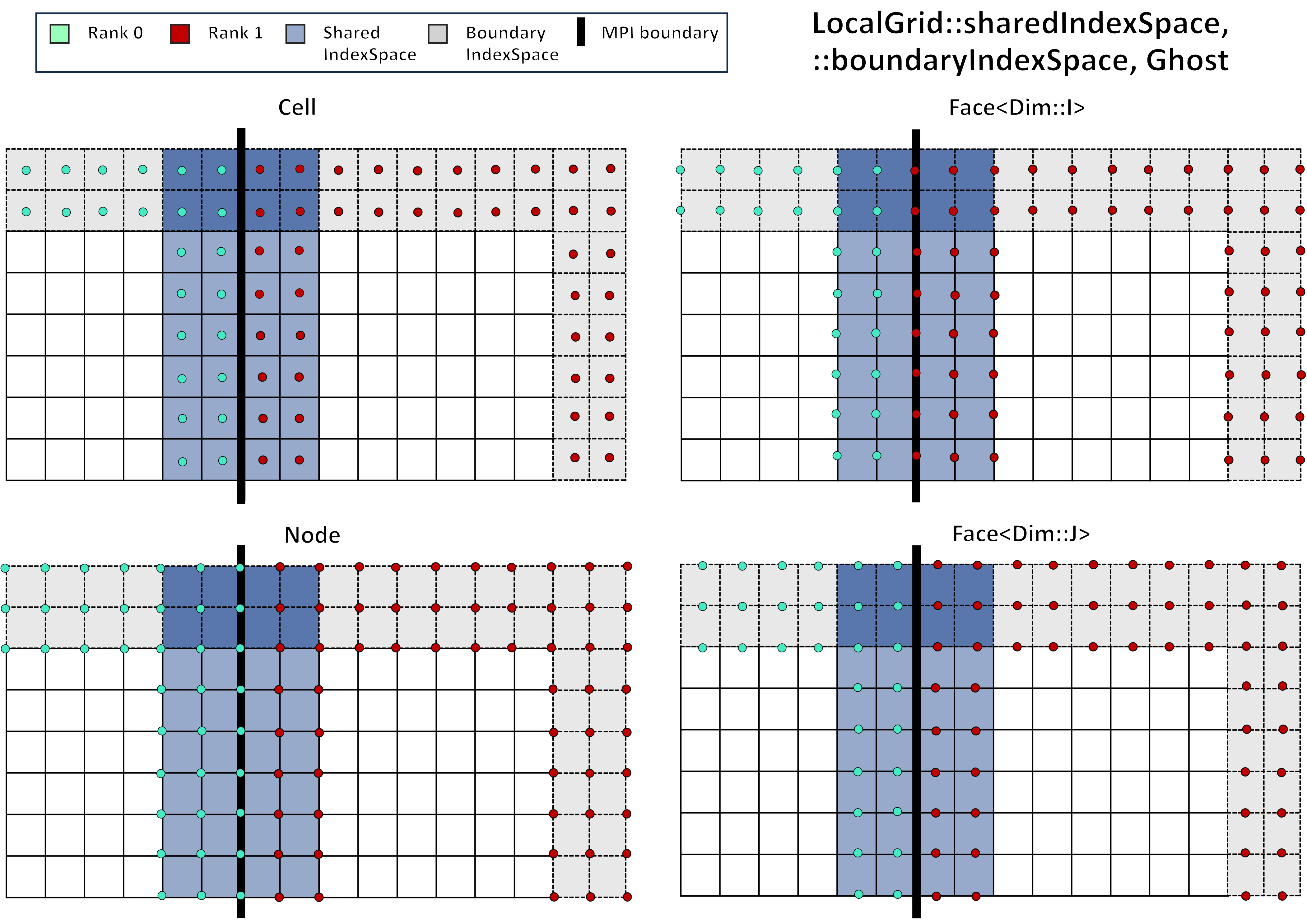
or include ghosted entites (Ghost), depending on the user's physics:

In addition, shared index spaces define the regions within the halo width of the MPI boundary, while boundary index spaces are regions within the halo width of the global domain. Note that if the system is periodic there are no global boundaries and therfore every boundary index space is empty. Examples of shared and boundary index spaces for Own (without ghosts) are within the local system boundaries:
These shared or boundary index spaces can similarly be created with Ghost indexing included, which can be outside the local system boundaries:
auto global_grid = Cabana::Grid::createGlobalGrid( MPI_COMM_WORLD, global_mesh,
is_dim_periodic, partitioner );
int halo_width = 2;
auto local_grid = Cabana::Grid::createLocalGrid( global_grid, halo_width );This is part of the Programming Guide series
Cabana - A Co-Designed Library for Exascale Particle Simulations