-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 50
Core Neighbor Lists
Two different methods of neighbor list generation are available within Cabana. Verlet lists use a grid to speed up the search for nearby particles, while the (experimental) ArborX based lists use tree structures.
In the figure below all neighbors are shown in yellow for the example central particle (red) within a specified cutoff radius.
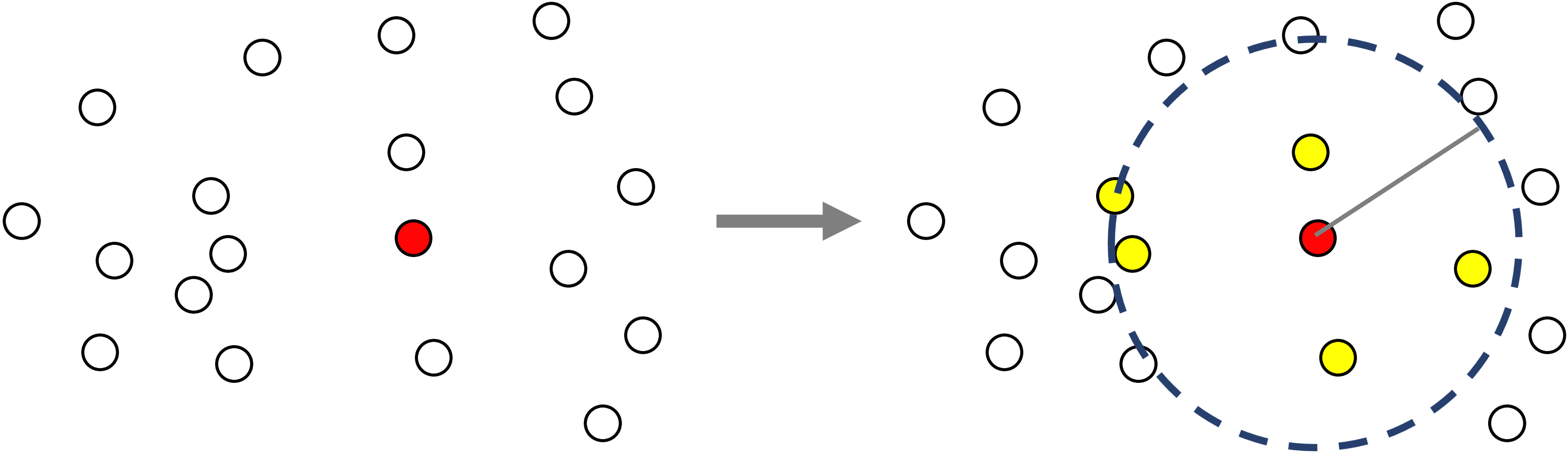
Given a list of particle positions, for every particle in the list a Verlet list computes the other particles in the list that are within some specified cutoff distance from the particle, accelerated by a linked cell grid decomposition. Once created, the Verlet list data can be accessed with the neighbor list interface.
Header File: Cabana_VerletList.hpp
Usage: Creating a neighbor list via a Verlet List
template<class MemorySpace,class AlgorithmTag,class LayoutTag,class BuildTag>
class VerletList-
MemorySpace: The memory space in which the neighbor list data will be allocated -
AlgorithmTag: Algorithm type indicator. Valid parameters areFullNeighborTagfor building full neighbor lists andHalfNeighborTagfor building half neighbor lists. -
LayoutTag: Data layout indicator. Valid parameters areVerletLayoutCSRfor using compressed sparse row andVerletLayout2Dfor using a two dimensional array. -
BuildTag: Hierarchical parallel build indicator. Valid parameters areTeamOpTagandTeamVectorOpTag
Example: Verlet List Tutorial
Example: Verlet List Unit Test
// Define data including particle coordinates
using DataTypes = Cabana::MemberTypes<double[3],int>;
using DeviceType = Kokkos::Device<Kokkos::Serial, Kokkos::HostSpace>;
Cabana::AoSoA<DataTypes,DeviceType> aosoa( num_tuple );
auto positions = slice<0>( aosoa );
// Define the bounding box of the grid
double grid_min[3] = {0.0,0.0,0.0};
double grid_max[3] = {3.0,3.0,3.0};
// Create the neighbor list for particles within a given radius.
double neighborhood_radius = 0.25;
double cell_ratio = 1.0;
using ListAlgorithm = Cabana::FullNeighborTag;
using ListLayout = Cabana::VerletLayoutCSR;
using ListType = Cabana::VerletList<DeviceType,ListAlgorithm,ListLayout>;
ListType verlet_list( positions, 0, positions.size(),
neighborhood_radius, cell_ratio,
grid_min, grid_max );
Given a list of particle positions, for every particle in the list an ArborX tree list computes the other particles in the list that are within some specified cutoff distance from the particle, as with the Verlet list.
Header File: Cabana_Experimental_NeighborList.hpp
Usage: Creating a neighbor list via ArborX
template <typename MemorySpace, typename Tag>
struct CrsGraph
template <typename MemorySpace, typename Tag>
struct DenseWhere CrsGraph is used for the compressed storage layout (makeNeighborList)
and Dense for the full 2D storage layout (make2DNeighborList).
-
MemorySpace: The memory space in which the neighbor list data will be allocated -
Tag: Algorithm type indicator. Valid parameters areFullNeighborTagfor building full neighbor lists andHalfNeighborTagfor building half neighbor lists.
Example: Neighbor List with ArborX Tutorial
Example: ArborX List Unit Test
// Define data including particle coordinates
using DataTypes = Cabana::MemberTypes<double[3],int>;
using DeviceType = Kokkos::Device<Kokkos::Serial, Kokkos::HostSpace>;
Cabana::AoSoA<DataTypes,DeviceType> aosoa( num_tuple );
auto positions = slice<0>( aosoa );
// Create the neighbor list for particles within a given radius.
double neighborhood_radius = 0.25;
auto nlist = Cabana::Experimental::makeNeighborList<device_type>(
Cabana::FullNeighborTag{}, positions, 0, positions.size(), test_radius );
This is part of the Programming Guide series
Cabana - A Co-Designed Library for Exascale Particle Simulations