RPC is a powerful technique for constructing distributed, client-server based applications. It is based on extending the notion of conventional, or local procedure calling, so that the called procedure need not exist in the same address space as the calling procedure. The two processes may be on the same system, or they may be on different systems with a network connecting them. By using RPC, programmers of distributed applications avoid the details of the interface with the network. The transport independence of RPC isolates the application from the physical and logical elements of data communications mechanism and allows the application to use a variety of transports.
RPC makes the client/server model of computing more powerful and easier to program. When combined with the ONC RPCGEN protocol compiler clients transparently make remote calls through a local procedure interface.
An RPC is analogous to a function call. Like a function call, when an RPC is made, the calling arguments are passed to the remote procedure and the caller waits for a response to be returned from the remote procedure.
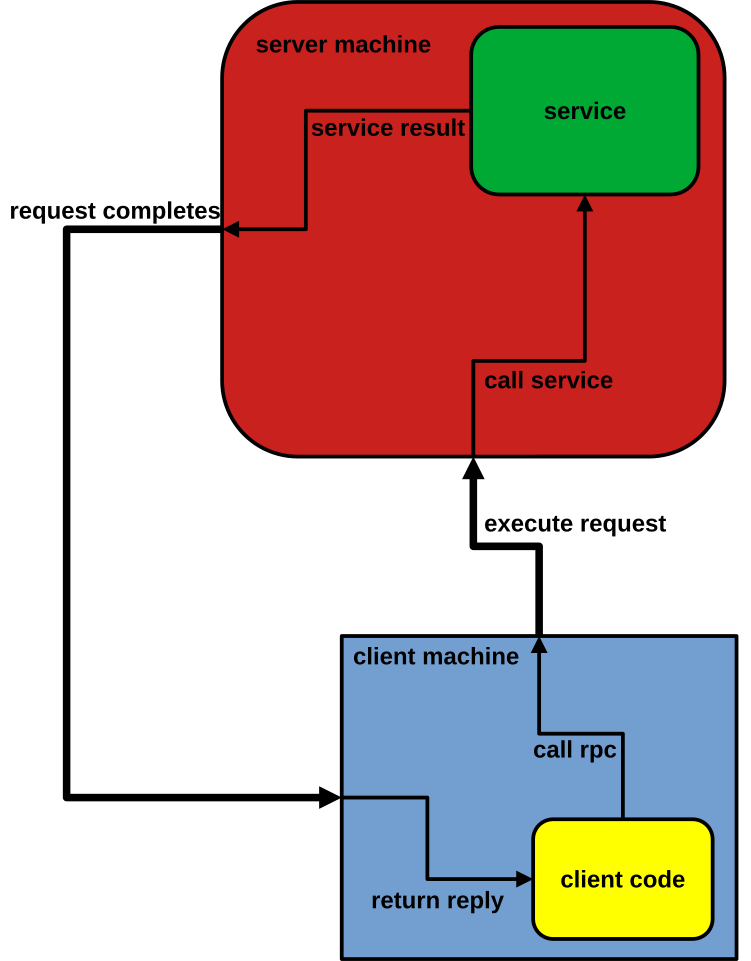
Figure shows the flow of activity that takes place during an RPC call between two networked systems. The client makes a procedure call that sends a request to the server and waits. The thread is blocked from processing until either a reply is received, or it times out. When the request arrives, server calls a dispatch routine that performs the requested service, and sends the reply to the client. After the RPC call is completed, the client program continues. RPC specifically supports network applications.
Remote Procedure Calling Mechanism A remote procedure is uniquely identified by the triple:
program number,
version number,
procedure number.
The program number identifies a group of related remote procedures, each of which has a unique procedure number. A program may consist of one or more versions. Each version consists of a collection of procedures which are available to be called remotely. Version numbers enable multiple versions of an RPC protocol to be available simultaneously. Each version contains a a number of procedures that can be called remotely. Each procedure has a procedure number.
Development process of RPC Application.